Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a common medical condition in men over the age of 50. It is characterized by an increase in the size of the prostate gland, which can lead to symptoms such as frequent urination, urgency, weak stream of urine, pain or burning during urination, and difficulty emptying the bladder completely.
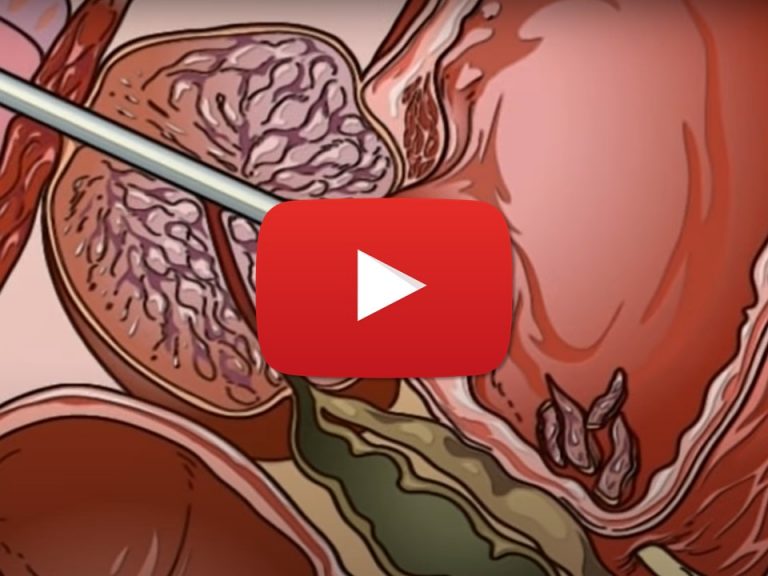
Reference technique: Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
The gold standard technique for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia is transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). TURP is a surgical procedure that involves the use of an endoscope to remove the parts of the prostate that obstruct the urethra.
TURP remains a safe and effective option for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia but requires a hospital stay of a few days and a recovery time of about six weeks. More modern techniques are being evaluated or are already in routine use, such as robotic surgery or laser surgery,
The surgery of tomorrow: laser and robot-assisted surgery
Robotic enucleation involves the use of a surgical surgical robot to remove the entire enlarged prostate adenoma, while laser surgery uses beams of light to vaporize the prostate tissue.
These surgical techniques are increasingly used because of their precision and effectiveness. They also allow for a faster recovery and shorter hospitalization than traditional surgical techniques.